Water is a critical resource in data centres, where it is used for cooling, humidification, and other processes. However, the demand for water has raised concerns about sustainability, particularly in regions that are already experiencing water scarcity. To address this issue, data centres have started adopting sustainable water treatment solutions that enable water recycling, reuse, and recovery. This blog explores the data centre water treatment options available, including direct nanofiltration (dNF), reverse osmosis (RO), water softening, and other methods, as well as the pros and cons of the types of water treatment.

Data centre water usage in Europe
According to a 2020 report by the European Data Center Association (EUDCA), the average water usage effectiveness (WUE)* for data centres in Europe was 1.40. This means that for every litre of water used for cooling, 0.40 litres were lost to evaporation, leaks, or other factors.
The same report found that the average WUE for data centres in Europe had improved significantly from 2015 to 2020, dropping from 1.85 to 1.40. This is largely due to the increased adoption of water-efficient cooling technologies and the implementation of more comprehensive water management strategies.
However, there is still much room for improvement in this area. The report also noted that the water usage of individual data centres varied greatly, with some facilities achieving WUEs as low as 1.05 while others had WUEs as high as 2.5. In addition to improving water quality, this suggests that there are still many data centres, big and small, that could benefit from more efficient data centre water treatment management practises.
Some of Europe’s largest data centre operators have taken a proactive step by committing to a plan for self-regulation. In 2021, the “Climate Neutral Data Centre Pact” was launched by major operators with the goal of making data centres in the region carbon neutral by 2030. One of the key objectives of the pact is to promote more sustainable water usage practices in data centres, including reducing overall water consumption and optimizing the use of water recovery and water recycling practices to further reduce their environmental impact and improve sustainability.
This is a timely move given that the information communication technology sector will experience huge growth over the coming years, with 29.3 billion devices expected online by 2030 (up from 18.4 billion in 2018). This massive increase in connected devices will require ever more data centres – facilities that house IT infrastructure for running applications and services, and for storing associated data. They consume water in two ways: directly through cooling processes for the servers and indirectly through electricity generation.
Why is water treatment important for data centres?
Water is an extremely efficient and cost-effective method for cooling data centres due to its high specific heat capacity compared to air. This means that water can absorb more heat without experiencing a significant temperature increase. For instance, let’s consider the amount of water and air required to cool an 8kW server rack. While 3200 m3/hour of air would be needed, only 2 m3/hour of water would suffice, demonstrating the significant difference in heat transfer efficiency.
The importance of data centre water treatment cannot be overstated. Because water is such an effective medium for cooling, it is often used in cooling systems. However, if the water is not properly treated, it can become contaminated and cause problems in the cooling system. Contaminants such as minerals, bacteria, and algae can build up in the water and cause corrosion, clogging, and other issues. Implementing a comprehensive water treatment programme is crucial to avoid issues caused by contaminated water in the cooling system. Water treatment for data centres keeps the water clean and free from contaminants and can help maintain the cooling system’s efficiency and reliability, which is essential for the operation of the data centre.
Make-up water used in cooling towers for data centres often contains inorganic salts such as potassium, sodium, calcium, and magnesium, all of which are cations and other dissolved solids like bicarbonates, carbonates, sulphates, chlorides, and nitrates which are known as anions. These contaminants can lead to issues such as fouling, scale formation, corrosion, and biological growth. In addition, pathogenic microorganisms like Legionella bacteria need to be neutralized. Therefore, effective treatment and disinfection of cooling tower water are crucial for meeting the unique demands of data centre cooling, which differ from those of other industrial sectors.
Types of water treatment for data centre cooling
There are several water treatment technologies for data centres, and each serves a specific purpose in maintaining water quality and protecting equipment. The following are some common water treatment methods used in data centres, with each explored in the next sections:
- Water softening
- Reverse osmosis
- Direct nanofiltration (dNF)
- Filtration and other methods
Water softening
Water softening can be achieved through ion exchange technology which involves passing water through a resin bed that exchanges hardness ions with sodium ions using an ion exchange resin. This process results in soft water that is free of minerals that scale buildup, which can reduce cooling efficiency and damage equipment over time.
By using water softening, the cooling equipment can operate more efficiently and effectively, leading to lower energy costs and reduced downtime due to equipment failure. It also helps to prolong the lifespan of the cooling equipment, which reduces maintenance and replacement costs over time. However, traditional water softener systems often carry high running costs, requiring large volumes of salt and water for regeneration processes. Most of the costs are associated with running regeneration cycles too long, and a lack of automation and monitoring of effluent flows. Cycles often work on a timer basis so in periods of lower flow, you could be creating excess waste streams.
Next-generation EcoSave water softening technologies offer a cost-effective way of preventing scale while limiting the cost of salt and water for regeneration processes. The technology incorporated into Envirogen’s EcoSave water softener system takes the guesswork out of regeneration cycles, realising the full benefits of water softeners. Advanced conductivity sensors detect the moment the ion exchange resins are regenerated and stop the rinsing cycles. This, combined with a counter-current regeneration flow, means EcoSave systems generate up to 80% less effluent water and use up to 60% less salt than conventional softeners.

Reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis water system technology (RO) uses a semi-permeable membrane to remove dissolved solids, organic matter, and other impurities from water. It is a commonly used treatment method in data centres, where it’s often used to treat the makeup water that is used in the cooling system. Makeup water is the additional water that is added to the cooling system to replace any water that is lost due to evaporation or leaks. If the makeup water is not properly treated, it can become contaminated with minerals, bacteria, and other impurities that can cause scaling, corrosion, and other issues in the cooling system.
RO is an effective way to remove these impurities and ensure that the makeup water is clean and free of contaminants. It’s also an environmentally friendly solution, as it reduces the need for chemical treatments that can be harmful to the environment. One potential downside of using RO for data centre water treatment cooling is that it can be energy-intensive. The process requires a significant amount of pressure and energy to force the water through the membrane, which can increase the energy consumption of the cooling system. However, the benefits of using clean, high-quality water in the cooling system may outweigh the energy costs associated with using RO.
Envirogen reverse osmosis water systems are based on various fundamental features, depending on the product and application. Our systems typically recover around 75% of incoming water streams. For even greater efficiency, nanofiltration modules can be added to filter the concentrate and achieve an overall 90% water recovery rate, which ensures that only a small amount of the incoming water stream is sent to drain as waste. We also offer a range of optional variable-speed pumps for improved process control and energy efficiency.
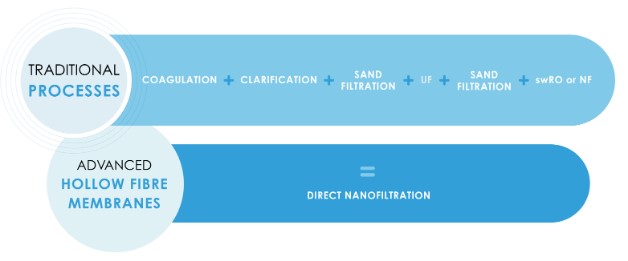
Direct nanofiltration – water recovery, water recycle and reuse with advanced hollow fiber membranes
Direct nanofiltration (dNF) is a membrane filtration technology that uses a semi-permeable membrane to remove dissolved solids, organic matter, and other impurities from water. It is a sustainable solution that can be used to treat wastewater and produce high-quality water that can be reused for non-potable purposes such as cooling.
Envirogen’s PureSep NF systems are highly innovative and are often used as a single-step replacement for multiple process stages, including coagulation, clarification, sand filtration, ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis. The PureSep nanofiltration plant also has a low chemical requirement and delivers significant energy savings and carbon footprint reductions too, when compared with conventional technologies, such as reverse osmosis, adsorption and oxidation.
For performance assessment and optimal system design we offer lab-scale bench-top pilot testing; and skid-based PureSep NF membrane pilot plant trials for on-site testing. The PureSep NF pilot plants are mounted to skids with forklift slots for easy offloading and on-site positioning. They allow for long-term testing, allowing you to gain thorough insights into the behaviour of our dNF membranes for data centre water treatment, over a longer period, continuously. Datalogging allows for in-depth analysis of the test results.
Filtration and other water treatment for data centres
Filtration is a key method for removing impurities and contaminants from water. There are various types of filters available, including sand filters, activated carbon filters, and multimedia filters. These filters can be installed at different stages of the water treatment process, depending on the level of filtration required and can be used alone or in combination with other treatment methods to produce high-quality water that can be reused for cooling and other operational purposes. Other treatment methods that can be used including UV disinfection and ozonation.
Envirogen water technical support services
At Envirogen we offer a range of services to help data centres optimize their cooling systems and improve their water and energy usage. Led by our expert process engineers, we will collaborate with you, helping clarify your specific needs, from initial consultation, through to post-installation service and maintenance support:
- FREE SITE ASSESSMENTS to identify the most efficient methods for saving energy, water, waste and money.
- A core range of proven modular water technologyfor your entire water treatment process.
- PureCare RemoteView remote water monitoring technology, designed to optimise performance and minimise downtime. PureCare RemoteView is secure, resilient, and created with the highest level of end-to-end cybersecurity in line with international security standards, plus industry 4.0 guidelines to ensure that your operation is fully resilient.
- Retrofit and plant refurbishment or plant upgrade services to extend the life of your data centre water treatment plant by reviewing and upgrading specific parts of your system.
- Mobile water treatment systems guarantee streams of purified water even if your demand or current supply changes dramatically, such as when switching from surface water to groundwater. Envirogen can provide temporary rental or permanent mobile equipment to help maintain the water quality used in the cooling system.
- 24/7 service backup and support – comprehensive support from our team of expert engineers who provide regular servicing and maintenance checks and emergency breakdown cover, should you need it.
Overall, we provide agile thinking, quick decision-making and many years of expertise to each project and we’ll work with your team to design flexible and innovative solutions to meet your exact data centre water treatment needs.

Summary: Sustainable water treatment solutions for data centres
Water usage is a significant sustainability challenge that requires innovative and sustainable solutions. Water treatment technologies for data centres, such as dNF, RO, and water softening can be used to produce high-quality water that can be reused for cooling and other operational purposes. These technologies have their own advantages and disadvantages, and data centre operators need to consider their specific needs and operational requirements when choosing a water treatment solution. The adoption of sustainable water treatment solutions for data centres can not only reduce water consumption but also promote water sustainability in the data centre industry. The data centre water usage effectiveness (WUE) metric, mentioned above, can also be used to measure the efficiency of water usage in data centres and drive improvements in this area.
As businesses continue to move to the cloud and consumers demand more data-hungry services, the demand for water will only increase. That’s why it’s important for businesses to be aware of the impact their move to the cloud could have on our environment and take steps to mitigate it. Fortunately, there are many conscious companies working on innovative solutions to reduce water usage in data centres. So, while there is still work to be done, there is reason for optimism when it comes to reducing the impact of the data centres on our environment.
*Data Centre Water Usage Effectiveness (WUE) is a metric that measures the amount of water used in a data centre relative to the amount of IT equipment it supports. The metric is expressed as the ratio of the total facility water usage to the IT equipment energy usage. A lower WUE value indicates more efficient water usage, which can help reduce the environmental impact of data centres.
Get started on your data centre water treatment plan. Request your FREE, no-obligation assessment on how you can save energy, water, waste and money
